Compare Strategies
| STRAP | LONG CALL LADDER | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| About Strategy |
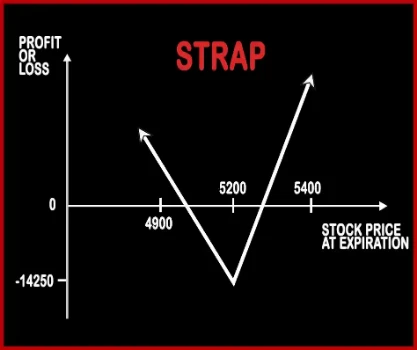
Strap Option StrategyStrap Strategy is similar to Long Straddle, the only difference is the quantity traded. A trader will buy two Call Options and one Put Options. In this strategy, a trader is very bullish on the market and volatility on upside but wants to hedge himself in case the stock doesn’t perform as per his expectations. This strategy will make more profits compared to long straddle sin |
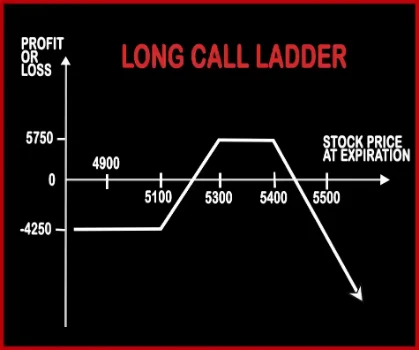
Long Call Ladder Option StrategyLong Call Ladder Strategy is an extension to Bull Call Spread Strategy. A trader will be slightly bullish about the market, in this strategy but bearish over volatility. It involves buying of an ITM Call Option and sale of 1 ATM & 1 OTM Call Options. However, the risk associated with this strategy is unlimited and reward is limited. |
STRAP Vs LONG CALL LADDER - Details
| STRAP | LONG CALL LADDER | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Neutral | Neutral |
| Type (CE/PE) | CE (Call Option) + PE (Put Option) | CE (Call Option) |
| Number Of Positions | 3 | 3 |
| Strategy Level | Beginners | Advance |
| Reward Profile | Profit Achieved When Price of Underlying > Strike Price of Calls/Puts + (Net Premium Paid/2) OR Price of Underlying < Strike Price of Calls/Puts - Net Premium Paid | Unlimited |
| Risk Profile | Max Loss Occurs When Price of Underlying = Strike Price of Calls/Puts | Unlimited |
| Breakeven Point | Strike Price of Calls/Puts + (Net Premium Paid/2) | Upper Breakeven Point = Total Strike Prices of Short Calls - Strike Price of Long Call - Net Premium Paid, Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Long Call + Net Premium Paid |
STRAP Vs LONG CALL LADDER - When & How to use ?
| STRAP | LONG CALL LADDER | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Neutral | Neutral |
| When to use? | This strategy is used when the investor is bullish on the stock and expects volatility in the near future. | This Strategy is an extension to Bull Call Spread Strategy. A trader will be slightly bullish about the market, in this strategy but bearish over volatility. |
| Action | Buy 2 ATM Call Option, Buy 1 ATM Put Option | Buy 1 ITM Call, Sell 1 ATM Call, Sell 1 OTM Call |
| Breakeven Point | Strike Price of Calls/Puts + (Net Premium Paid/2) | Upper Breakeven Point = Total Strike Prices of Short Calls - Strike Price of Long Call - Net Premium Paid, Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Long Call + Net Premium Paid |
STRAP Vs LONG CALL LADDER - Risk & Reward
| STRAP | LONG CALL LADDER | |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Profit Scenario | UNLIMITED | Strike Price of Lower Strike Short Call - Strike Price of Long Call - Net Premium Paid - Commissions Paid |
| Maximum Loss Scenario | Net Premium Paid | Price of Underlying - Upper Breakeven Price + Commissions Paid |
| Risk | Limited | Unlimited |
| Reward | Unlimited | Unlimited |
STRAP Vs LONG CALL LADDER - Strategy Pros & Cons
| STRAP | LONG CALL LADDER | |
|---|---|---|
| Similar Strategies | Strip, Short Put Ladder, Short Call Ladder | Short Strangle (Sell Strangle), Short Straddle (Sell Straddle) |
| Disadvantage | • To generate profit, there should be significant change in share price. • Expensive strategy. | • Unlimited risk. • Margin required. |
| Advantages | • Limited loss. • If share prices are moving then traders can book unlimited profit. • A trader can still book profit if the underlying falls substantially. | • Reduces capital outlay of bull call spread. • Wider maximum profit zone. • When there is decrease in implied volatility, this strategy can give profit. |