Compare Strategies
| COVERED CALL | LONG STRANGLE | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| About Strategy |
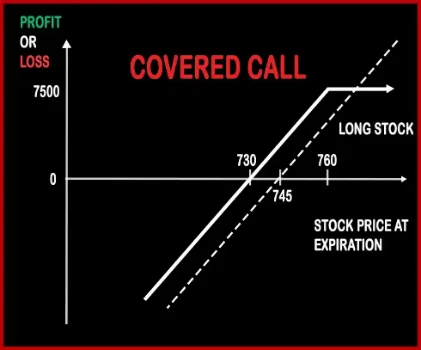
Covered Call Option StrategyMr. X owns Reliance Shares and expects the price to rise in the near future. Mr. X is entitled to receive dividends for the shares he hold in cash market. Covered Call Strategy involves selling of OTM Call Option of the same underlying asset. The OTM Call Option Strike Price will generally be the price, where Mr. X will look to get out o |
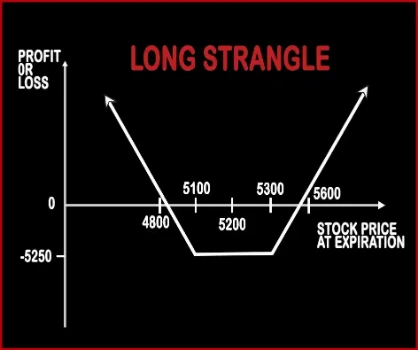
Long Strangle Option StrategyA Strangle is similar to Straddle. In Strangle, a trader will purchase one OTM Call Option and one OTM Put Option, of the same expiry date and the same underlying asset. This strategy will reduce the entry cost for trader and it is also cheaper than straddle. A trader will make profits, if the market moves sharply in either direction and gives extra-ordinary returns in the .. |
COVERED CALL Vs LONG STRANGLE - Details
| COVERED CALL | LONG STRANGLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Bullish | Neutral |
| Type (CE/PE) | CE (Call Option) | CE (Call Option) + PE (Put Option) |
| Number Of Positions | 2 | 2 |
| Strategy Level | Advance | Beginners |
| Reward Profile | Limited | Unlimited |
| Risk Profile | Unlimited | Limited |
| Breakeven Point | Purchase Price of Underlying- Premium Received | Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Put - Net Premium, Upper Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Call + Net Premium |
COVERED CALL Vs LONG STRANGLE - When & How to use ?
| COVERED CALL | LONG STRANGLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Bullish | Neutral |
| When to use? | An investor has a short term neutral view on the asset and for this reason holds the asset long and has a short position to generate income. | This strategy is used in special scenarios where you foresee a lot of volatility in the market due to election results, budget, policy change, annual result announcements etc. |
| Action | (Buy Underlying) (Sell OTM Call Option) | Buy OTM Call Option, Buy OTM Put Option |
| Breakeven Point | Purchase Price of Underlying- Premium Received | Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Put - Net Premium, Upper Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Call + Net Premium |
COVERED CALL Vs LONG STRANGLE - Risk & Reward
| COVERED CALL | LONG STRANGLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Profit Scenario | [Call Strike Price - Stock Price Paid] + Premium Received | Profit = Price of Underlying - Strike Price of Long Call - Net Premium Paid |
| Maximum Loss Scenario | Purchase Price of Underlying - Price of Underlying) + Premium Received | Max Loss = Net Premium Paid |
| Risk | Unlimited | Limited |
| Reward | Limited | Unlimited |
COVERED CALL Vs LONG STRANGLE - Strategy Pros & Cons
| COVERED CALL | LONG STRANGLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Similar Strategies | Bull Call Spread | Long Straddle, Short Strangle |
| Disadvantage | • Unlimited risk, limited reward. • Inability to earn interest on the proceed used to buy the underlying stock. | • Require significant price movement to book profit. • Traders can lose more money if the underlying asset stayed stagnant. |
| Advantages | • Profit from option premium, rise in the underlying stock and dividends on the stock. • Allows you to generate income from your holding. • Profit when underlying stock price rise, move sideways or marginal fall. | • Able to book profit, no matter if the underlying asset goes in either direction. • Limited loss to the debit paid. • If the underlying asset continues to move in one direction then you can book Unlimited profit . |