Compare Strategies
| LONG STRANGLE | SHORT STRANGLE | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| About Strategy |
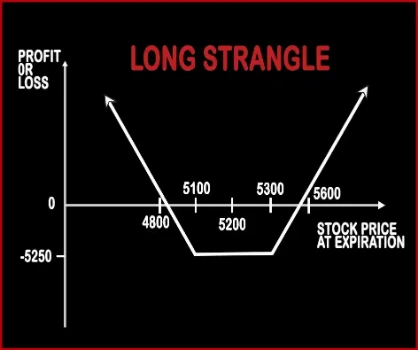
Long Strangle Option StrategyA Strangle is similar to Straddle. In Strangle, a trader will purchase one OTM Call Option and one OTM Put Option, of the same expiry date and the same underlying asset. This strategy will reduce the entry cost for trader and it is also cheaper than straddle. A trader will make profits, if the market moves sharply in either direction and gives extra-ordinary returns in the |
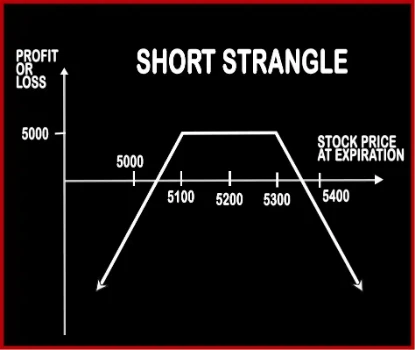
Short Strangle Option StrategyThis strategy is similar to Short Straddle; the only difference is of the strike prices at which the positions are built. Short Strangle involves selling of one OTM Call Option and selling of one OTM Put Option, of the same expiry date and same underlying asset. Here the probability of making profits is more as there is a spread between the two strike prices, and if .. |
LONG STRANGLE Vs SHORT STRANGLE - Details
| LONG STRANGLE | SHORT STRANGLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Neutral | Neutral |
| Type (CE/PE) | CE (Call Option) + PE (Put Option) | CE (Call Option) + PE (Put Option) |
| Number Of Positions | 2 | 2 |
| Strategy Level | Beginners | Advance |
| Reward Profile | Unlimited | Limited |
| Risk Profile | Limited | Unlimited |
| Breakeven Point | Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Put - Net Premium, Upper Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Call + Net Premium | Lower Break-even = Strike Price of Put - Net Premium, Upper Break-even = Strike Price of Call+ Net Premium |
LONG STRANGLE Vs SHORT STRANGLE - When & How to use ?
| LONG STRANGLE | SHORT STRANGLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Neutral | Neutral |
| When to use? | This strategy is used in special scenarios where you foresee a lot of volatility in the market due to election results, budget, policy change, annual result announcements etc. | This strategy is perfect in a neutral market scenario when the underlying is expected to be less volatile. |
| Action | Buy OTM Call Option, Buy OTM Put Option | Sell OTM Call, Sell OTM Put |
| Breakeven Point | Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Put - Net Premium, Upper Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Call + Net Premium | Lower Break-even = Strike Price of Put - Net Premium, Upper Break-even = Strike Price of Call+ Net Premium |
LONG STRANGLE Vs SHORT STRANGLE - Risk & Reward
| LONG STRANGLE | SHORT STRANGLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Profit Scenario | Profit = Price of Underlying - Strike Price of Long Call - Net Premium Paid | Maximum Profit = Net Premium Received |
| Maximum Loss Scenario | Max Loss = Net Premium Paid | Loss = Price of Underlying - Strike Price of Short Call - Net Premium Received |
| Risk | Limited | Unlimited |
| Reward | Unlimited | Limited |
LONG STRANGLE Vs SHORT STRANGLE - Strategy Pros & Cons
| LONG STRANGLE | SHORT STRANGLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Similar Strategies | Long Straddle, Short Strangle | Short Straddle, Long Strangle |
| Disadvantage | • Require significant price movement to book profit. • Traders can lose more money if the underlying asset stayed stagnant. | • Unlimited loss is associated with this strategy, not recommended for beginners. • Limited reward amount. |
| Advantages | • Able to book profit, no matter if the underlying asset goes in either direction. • Limited loss to the debit paid. • If the underlying asset continues to move in one direction then you can book Unlimited profit . | • Higher chance of profitability due to selling of OTM options. • Advantage from double time decay and a contraction in volatility. • Traders can book profit when underlying asset stays within a tight trading range. |