Compare Strategies
| SHORT CALL | SHORT CALL LADDER | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| About Strategy |
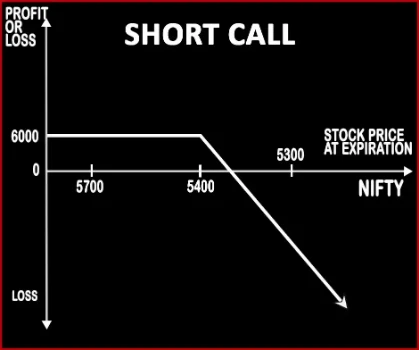
Short Call Option StrategyA trader shorts or writes a Call Option when he feels that underlying stock price is likely to go down. Selling Call Option is a strategy preferred for experienced traders. However this strategy is very risky in nature. If the stock rallies on the upside, your risk becomes potentially unquantifiable and unlimited. If the strategy |
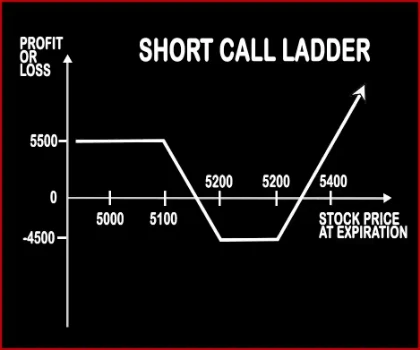
Short Call Ladder Option StrategyThis strategy is implemented when a trader is moderately bullish on the market, and volatility. It involves sale of an ITM Call Option, buying of an ATM Call Option & OTM Call Option. The risk associated with the strategy is limited. Risk:
|
SHORT CALL Vs SHORT CALL LADDER - Details
| SHORT CALL | SHORT CALL LADDER | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Bearish | Neutral |
| Type (CE/PE) | CE (Call Option) | CE (Call Option) |
| Number Of Positions | 1 | 3 |
| Strategy Level | Advance | Advance |
| Reward Profile | Limited | Unlimited |
| Risk Profile | Unlimited | Limited |
| Breakeven Point | Strike Price of Short Call + Premium Received | Upper Breakeven Point = Total Strike Prices of Long Calls - Strike Price of Short Call + Net Premium Received Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Short Call - Net Premium Received |
SHORT CALL Vs SHORT CALL LADDER - When & How to use ?
| SHORT CALL | SHORT CALL LADDER | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Bearish | Neutral |
| When to use? | It is an aggressive strategy and involves huge risks. It should be used only in case where trader is certain about the bearish market view on the underlying. | This strategy is implemented when a trader is moderately bullish on the market, and volatility |
| Action | Sell or Write Call Option | Sell 1 ITM Call, Buy 1 ATM Call, Buy 1 OTM Call |
| Breakeven Point | Strike Price of Short Call + Premium Received | Upper Breakeven Point = Total Strike Prices of Long Calls - Strike Price of Short Call + Net Premium Received Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Short Call - Net Premium Received |
SHORT CALL Vs SHORT CALL LADDER - Risk & Reward
| SHORT CALL | SHORT CALL LADDER | |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Profit Scenario | Max Profit = Premium Received | Profit Achieved When Price of Underlying > Total Strike Prices of Long Calls - Strike Price of Short Call + Net Premium Received |
| Maximum Loss Scenario | Loss Occurs When Price of Underlying > Strike Price of Short Call + Premium Received | Strike Price of Lower Strike Long Call - Strike Price of Short Call - Net Premium Received + Commissions Paid |
| Risk | Unlimited | Limited |
| Reward | Limited | Unlimited |
SHORT CALL Vs SHORT CALL LADDER - Strategy Pros & Cons
| SHORT CALL | SHORT CALL LADDER | |
|---|---|---|
| Similar Strategies | Covered Put, Covered Calls | Short Put Ladder, Strip, Strap |
| Disadvantage | • Unlimited risk to the upside underlying stocks. • Potential loss more than the premium collected. | • Unlimited risk. • Margin required. |
| Advantages | • With the help of this strategy, traders can book profit from falling prices in the underlying asset. • Less investment, more profit. • Traders can book profit when underlying stock price fall, move sideways or rise by a small amount. | • Higher probability of profit. • Unlimited upside profit. • Limited maximum loss. |