Compare Strategies
| LONG PUT LADDER | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| About Strategy |
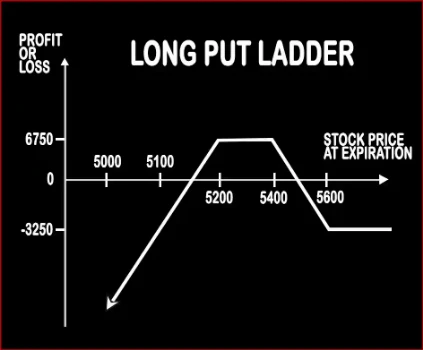
Long Put Ladder Option StrategyLong Put Ladder can be implemented when a trader is slightly bearish on the market and volatility. It involves buying of an ITM Put Option and sale of 1 ATM & 1 OTM Put Options. However, the risk associated with this strategy is unlimited and reward is limited. Risk:< |
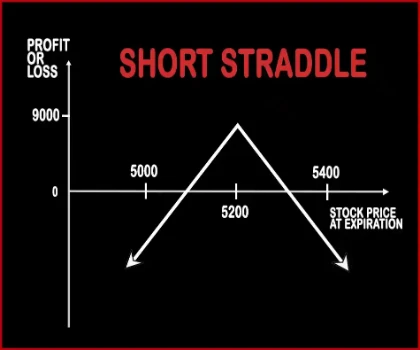
Short Straddle Option strategyThis strategy is just the opposite of Long Straddle. A trader should adopt this strategy when he expects less volatility in the near future. Here, a trader will sell one Call Option & one Put Option of the same strike price, same expiry date and of the same underlying asset. If the stock/index hovers around the same levels then both the options will expire worthless an .. |
LONG PUT LADDER Vs SHORT STRADDLE - Details
| LONG PUT LADDER | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Neutral | Neutral |
| Type (CE/PE) | PE (Put Option) | CE (Call Option) + PE (Put Option) |
| Number Of Positions | 3 | 2 |
| Strategy Level | Advance | Advance |
| Reward Profile | Limited | Limited |
| Risk Profile | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Breakeven Point | Upper Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Long Put - Net Premium Paid, Lower Breakeven Point = Total Strike Prices of Short Puts - Strike Price of Long Put + Net Premium Paid | Lower Breakeven = Strike Price of Put - Net Premium, Upper breakeven = Strike Price of Call+ Net Premium |
LONG PUT LADDER Vs SHORT STRADDLE - When & How to use ?
| LONG PUT LADDER | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Neutral | Neutral |
| When to use? | This Strategy can be implemented when a trader is slightly bearish on the market and volatility. | This strategy is work well when an investor expect a flat market in the coming days with very less movement in the prices of underlying asset. |
| Action | Buy 1 ITM Put, Sell 1 ATM Put, Sell 1 OTM Put | Sell Call Option, Sell Put Option |
| Breakeven Point | Upper Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Long Put - Net Premium Paid, Lower Breakeven Point = Total Strike Prices of Short Puts - Strike Price of Long Put + Net Premium Paid | Lower Breakeven = Strike Price of Put - Net Premium, Upper breakeven = Strike Price of Call+ Net Premium |
LONG PUT LADDER Vs SHORT STRADDLE - Risk & Reward
| LONG PUT LADDER | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Profit Scenario | Strike Price of Long Put - Strike Price of Higher Strike Short Put - Net Premium Paid - Commissions Paid | Max Profit = Net Premium Received - Commissions Paid |
| Maximum Loss Scenario | When Price of Underlying < Total Strike Prices of Short Puts - Strike Price of Long Put + Net Premium Paid | Maximum Loss = Long Call Strike Price - Short Call Strike Price - Net Premium Received |
| Risk | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Reward | Limited | Limited |
LONG PUT LADDER Vs SHORT STRADDLE - Strategy Pros & Cons
| LONG PUT LADDER | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Similar Strategies | Short Strangle (Sell Strangle), Short Straddle (Sell Straddle) | Short Strangle |
| Disadvantage | • Unlimited risk. • Margin required. | • Unlimited risk. • If the price of the underlying asset moves in either direction then huge losses can occur. |
| Advantages | • Reduces capital outlay of bear put spread. • Wider maximum profit zone. • When there is decrease in implied volatility, this strategy can give profit. | • A trader can earn profit even when there is no volatility in the market . • Allows you to benefit from double time decay. • Trader can collect premium from puts and calls option . |