Lagging Indicator: Explained, Types, and Importance
Define Lagging Indicator
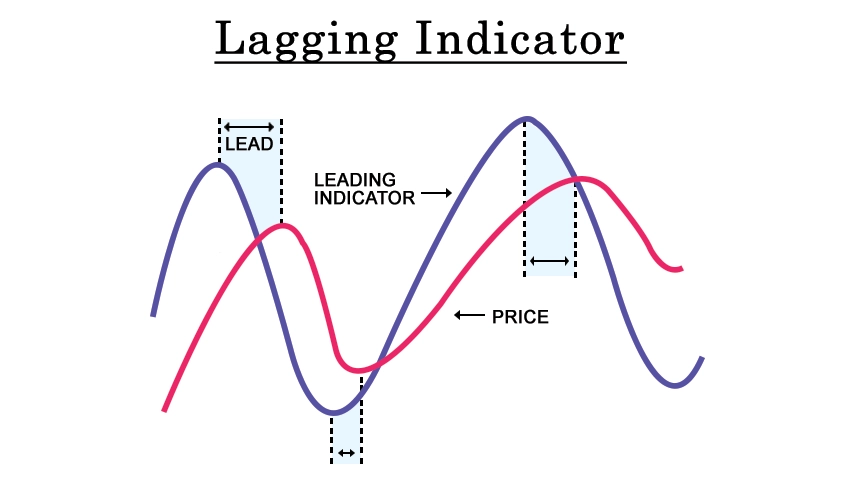
A lagging indicator is a type of economic or financial metric that follows or lags behind particular events or trends. It provides information or data about past events and is used to confirm or validate trends that have already occurred. Lagging indicators are often used to assess the overall health or performance of an economy, market, or business after a specific period has elapsed.
Lagging indicators are backward-looking and reflect changes that have already taken place. They are typically based on historical data and can include metrics such as unemployment rates, inflation rates, GDP growth rates, corporate earnings, or stock market performance. describe lagging indicator are valuable for providing a retrospective analysis and verifying the direction and extent of a trend or change.
While best lagging indicator are useful for assessing the impact or outcome of past events, they have limitations in terms of their predictive value for future trends. They can be helpful for understanding the current state of an economy or business, but they may not provide reliable insights into future developments. example of lagging indicator. Therefore, lagging indicators are often used in conjunction with leading indicators, which provide more forward-looking information, to gain a comprehensive understanding of economic or financial conditions.
Types of Lagging Indicators
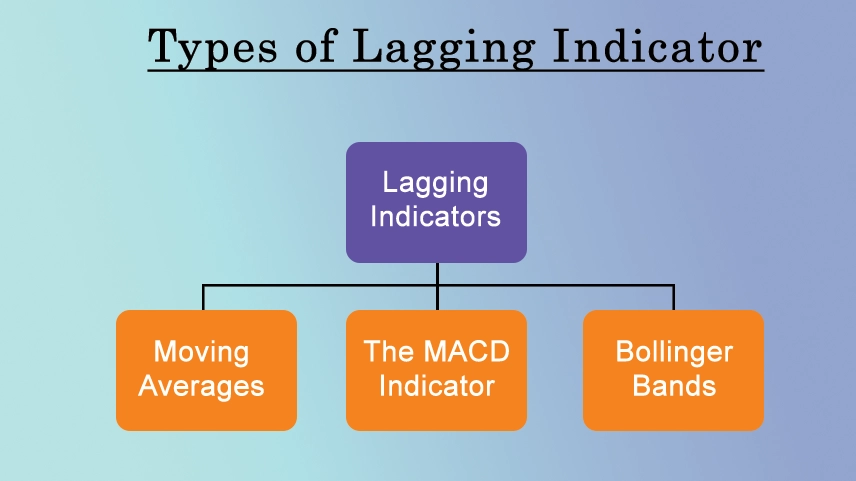
The different types of lagging indicators help in better grasping their definition. lagging indicators examples. what are the lagging indicators? types include: Moving average, MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), and Bollinger Bands are all examples of lagging indicators. Let's briefly discuss each of these types:
1. Moving Average: A moving average is a lagging indicator that calculates the average price of a security over a specified period of time. moving average analysis smooths out price fluctuations and helps identify trends. moving average indicator, Common moving averages include a simple moving average “SMA” & the exponential moving average (EMA).
2. MACD Indicator: About macd indicator The MACD is a popular lagging indicator that measures the relationship between two moving averages of a security's price. macd indicator analysis It consists of two lines: the MACD line and the signal line. When these lines cross, it can signal potential buy or sell opportunities.
3. Bollinger Bands: Bollinger Bands strategy are a lagging indicator that consists of a moving average (typically the simple moving average) and two standard deviation lines plotted above and below the moving average. Bollinger Bands use help identify volatility and potential price reversals. Bollinger bands indicator, they are the lagging indicator example.
Importance of Lagging indicators
The benefits of lagging indicators hold significant importance for various reasons:
1. Confirmation of trends: Lagging indicators help confirm the direction and magnitude of trends that have already occurred. By providing historical data, they validate whether a particular trend or change in the economy, market, or business has taken place, offering a more comprehensive understanding of the situation.
2. Performance evaluation: Lagging indicators are used to assess the overall performance of an economy, industry, or organization over a specific period. They provide insights into past outcomes, allowing for comparisons, trend analysis, and the identification of areas that need improvement or further attention.
3. Decision-making: Lagging indicators play a vital role in decision-making processes. By analyzing past data, decision-makers can evaluate the effectiveness of previous decisions, policies, or strategies. Lagging indicators enable a retrospective view of how various factors have impacted the outcomes, assisting in making informed choices for future actions.
4. Historical analysis and forecasting: Lagging indicators contribute to historical analysis by identifying patterns, correlations, and relationships between different variables. This information can be used to develop forecasting models and make predictions about future trends or outcomes, albeit with some limitations as lagging indicators focus on past events.
5. Stakeholder communication: Lagging indicators provide a basis for communicating with stakeholders, such as investors, shareholders, or the public. They offer tangible evidence of performance, achievements, and outcomes, fostering transparency and credibility in reporting.
6. Economic and policy evaluation: Lagging indicators are instrumental in evaluating the effectiveness of economic policies, government interventions, or regulatory measures. By assessing the impact of such actions through lagging indicators, policymakers can adjust their strategies and interventions to achieve desired outcomes.
Explained Lagging Indicator
A lagging indicator is a financial measure that becomes evident after a significant change has already occurred. These indicators validate long-term trends, but they do not serve as predictors. Lagging indicators are valuable because other leading indicators may be more volatile or subject to misleading short-term fluctuations. Therefore, analyzing all lagging indicators is one method to verify if an economic shift has indeed happened.
In simpler terms:
A lagging indicator is a financial signal that becomes visible only after a major change has already happened. It confirms the long-term trends but they cannot predict them. Lagging indicators are useful because other leading indicators can be more unpredictable or misleading in the short term. Therefore, studying lagging indicators is a way to confirm if there has been a significant shift in the economy.
Economic Lagging Indicators
Economic lagging indicators are measurements or data points that reflect changes in the economy after they have already occurred. They provide confirmation of past economic trends and are not used for predicting future shifts a lagging economic indicators is important because they help validate whether an economic change has actually taken place. Unlike leading indicators that provide early signals of potential changes, lagging indicators offer a retrospective view of the economy's performance. Examples of economic lagging indicators include unemployment rates, inflation levels, and gross domestic product (GDP) figures.
Business Lagging Indicators
Business lagging indicators are metrics or factors that provide insight into the performance and health of a business, but they do so after the events or changes have already taken place. These indicators are retrospective in nature and are used to assess the outcomes and results of past business activities or decisions. Lagging indicators help in evaluating the overall effectiveness and success of strategies, initiatives, or operational processes. Examples of business lagging indicators include financial statements (such as profit and loss statements, balance sheets), customer satisfaction ratings, employee turnover rates, and sales figures. By analyzing these lagging indicators, businesses can gain a better understanding of their past performance and make informed decisions for future improvements.
Technical Lagging Indicators
Technical lagging indicators are tools or signals used in technical analysis to assess price movements and market trends after they have already occurred. These indicators are derived from historical price data and provide retrospective insights into market behavior. lagging technical indicator. Unlike leading indicators that aim to forecast future price movements, lagging technical indicators are used to confirm or validate existing trends. They are often used to identify potential entry or exit points in trading strategies. Examples of technical lagging indicators include moving averages, MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), Bollinger Bands, and RSI (Relative Strength Index). Traders and analysts rely on these indicators to interpret past price patterns and make decisions based on the assumption that historical trends may repeat or continue in the future.
0 comments