Divident Investing: How it works, Risk of Dividend, Growth Strategy and Conclusion
What is Divident Investing
Dividend investing strategy where investors focus on purchasing stocks that pay regular dividends. Dividends are typically the portion of a company's earnings that are distributed to shareholders on the periodic basis, often quarterly. Companies that pay the dividends are usually well established & financially stable, generating consistent profits.
The primary goal of dividend investing is to generate the steady stream of passive income. Instead of relying solely on capital appreciation “the increase in a stock's price over time”, investors in dividend and paying stocks also benefit from regular dividend payments. These dividends can be the provide the reliable income stream, especially for retirees or those seeking supplemental income.
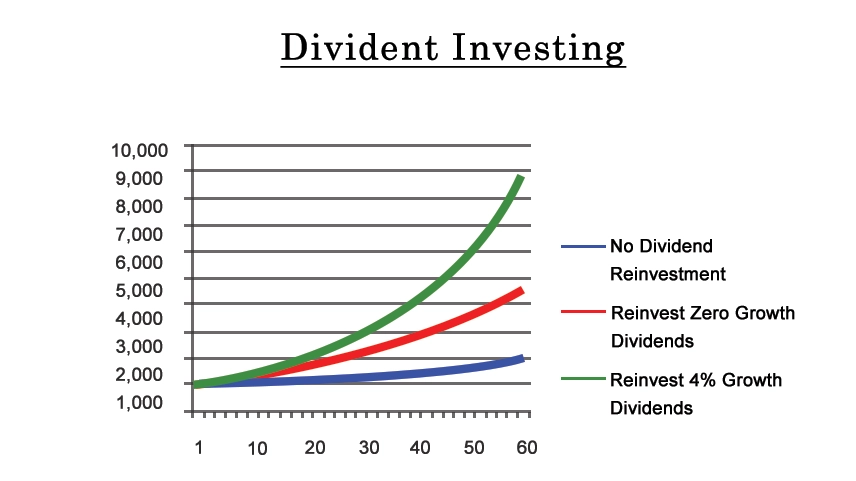
Dividend investing also offers the potential benefits in terms of the compounding. Investors can reinvest the dividends they can receive the back into the same stock or into other investments, dividend investing strategy which can be accelerate the growth of their investment portfolio over time.
How it works
Dividend investing works by investing in stocks of companies that regularly distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders in the form of dividends. Here's how it generally works:
1. Research and Selection: Investors begin by researching & selecting dividen paying stocks. This involves analyzing and the financial health of companies, their track record of dividend payments, dividend yield “the dividend amount relative to the stock price”, dividend growth rate, and other relevant factors. Investors often look for companies with a history of stable earnings and a commitment to returning value to shareholders through dividends.
2. Purchase of Stocks: Investors identified the suitable dividend paying stocks and they purchase shares through the brokerage account. They choose to invest in individual dividend paying stocks and opt for dividend focused mutual funds or exchange and traded funds “ETFs” that hold portfolios of dividend-paying stocks.
3. Receiving Dividends: Investors receive the dividends from the companies in which they are invested. Dividends are typically paid the quarterly basis, although some companies may pay them annually the semi-annually. The dividend amount per share is determined by the company's board of directors and is usually announced along with the company and financial results.
4. Reinvestment or Income: Investors have the option to use the dividends they receive in one of two ways:
• Reinvestment: Investors reinvest the dividends back into the same stock or into other investments. This can be done manually by purchasing additional shares and the dividend income received, or automatically through dividend reinvestment plans “DRIPs” offered by some companies and brokerage firms.
• Income: Alternatively, investors can choose to receive dividends of the cash income, which can provide the steady stream of passive income. This is particularly appealing for investors seeking regular income, such as the retirees.
5. Monitoring and Adjustment: Dividend investors typically monitor their investment and portfolio regularly to assess the performance of dividend paying stocks, track dividend payments, & evaluate any changes in the companies' fundamentals. Depending on individual the investment goals and market conditions, investors may adjust their portfolio by adding the new dividend paying stocks, selling underperforming ones, or the rebalancing their holdings.
Risk of Dividend
While dividend investing offers several advantages, it also comes with certain risks that investors should be aware of:
1. Dividend Cuts or Suspensions: Companies may reduce the suspend dividend payments during economic downturns, and financial difficulties, or periods of poor performance. Company's earnings decline, and cash flow weakens, or it needs to conserve capital for the other purposes, such as the debt repayment or meaning of dividend risk of dividend funds growth initiatives. Investors relying on dividend income may face the reduction in their expected cash flow if dividends are cut or suspended.
2. Market and Economic Risks: Dividend paying stocks are still subject to market and economic risks, just like any other stock. Factors such as the changes in interest rates, inflation, economic conditions, and market volatility can impact stock prices and dividend payments. In times of economic uncertainty or market downturns, dividend paying risk of dividend stocks may experience price declines, which can affect total returns for the investors.
3. Sector and Industry Risks: Certain sectors industries may be the more prone to dividend cuts or suspensions due to their sensitivity to the economic cycles, regulatory changes, technological disruptions, or other industry specific factors. For example, cyclical industries like energy and materials may the experience fluctuations in profitability and cash flow, risk of dividend investing affecting their ability to maintain dividend payments consistently.
4. Company-Specific Risks: Individual companies may face company-specific risks that could impact their ability to sustain the dividend payments. These risks include management changes, competitive pressures, regulatory issues, product recalls, litigation, and other unforeseen events. Investing in the diversified portfolio of dividend-paying stocks can help the mitigate some of these risks.
5. Inflation Risk: Inflation can erode the purchasing power of dividend income over time. While dividends may provide a steady stream of income, if the rate of inflation exceeds the growth rate of dividends, the real (inflation-adjusted) value of the income may decline. Investors should consider investments that have the potential to grow dividends over time to keep pace with inflation.
6. Interest Rate Risk: Dividend-paying stocks can be sensitive to changes in interest rates. When interest rates rise, dividend-paying stocks may become less attractive relative to fixed-income investments, leading investors to reallocate their portfolios. This can result in price declines for dividend-paying stocks.
Dividend Growth Strategy
The dividend growth strategy involves the investing in companies that consistently increase their dividend payments over time. Investors seek out companies with strong financial fundamentals and a commitment to rewarding shareholders through dividend growth. By prioritizing companies with sustainable dividend growth rates, manageable payout ratios, and a long-term perspective, investors aim to build a portfolio that generates a growing stream of passive income. Through regular monitoring and adjustments, diversification, and a focus on quality, dividend growth investors seek to capitalize on the combined benefits of increasing income and potential capital appreciation over the long term.
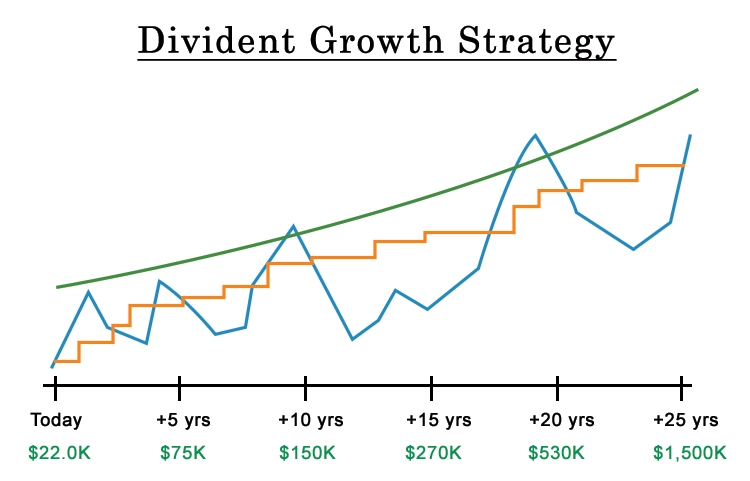
Conclusion
All this up, dividend growth investing offers investors a long-term, strategic way to accumulate wealth & earn passive income. Investors can benefit from the compounding impact of reestablish dividend investing chart, the prospect of capital appreciation and focusing on businesses that have the history of continually raising their dividends. This approach places a strong emphasis on long-term growth potential, dividend long-term viability and financial stability. Dividend growth & investors seek to maximize and returns as well as weather market fluctuations accomplishing and financial objectives through meticulous research, diversification, & consistent portfolio monitoring.
0 comments